Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is known and well studied. Currently, most of the workforce suffers from this disease. This type of osteochondrosis develops not only in the adult population, but is quite common in adolescents, the so-called juvenile osteochondrosis.
The cervical region is the most mobile part of the spine, so the load in this region is quite large. The disease develops gradually, is characterized by frequent exacerbations, which can lead to a significant decrease in the patient's quality of life.
Causes of the disease
The causes of the disease, as a rule, are various and may depend on the age of the patient. Let's highlight the most frequent:
- violation of calcium-phosphorus metabolism of any etiology;
- various traumatic back injuries;
- unbalanced load on the spine (physical inactivity or vice versa, the effect of increased load);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- congenital malformations of the spine;
- posture change, including scoliotic type;
- circulatory disorders leading to poor nutrition of the intervertebral disc;
- Age-related dystrophic disorders of bone tissue.

In adolescence, the main causes of the development of the disease are injuries, unbalanced physical activity (training process). In older patients, the main reason is a long-term habitual position during work, a violation of the hormonal background.
Other predisposing factors for the development of the disease can be:
- inheritance;
- hypothermia;
- exacerbation of osteochondrosis treated poorly or not completely;
- stressful situations and overwork.
Osteochondrosis develops gradually. A person who is constantly involved in sports may not realize that he is susceptible to this disease.
Most of this condition occurs in people over the age of twenty-five. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is characterized by the fact that the process develops from the upper sections. However, without medical attention, the process can gradually affect the lower segments of the spine.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in adults and children
As the disease develops over the years, in many cases the process is asymptomatic. Sometimes it happens that by chance using X-ray images you can determine the initial signs of the disease, while there will be no active complaints. It must be remembered that the older the patient, the more diverse complaints he will present.
The main complaints of cervical osteochondrosis are:
- frequent headache and dizziness;
- numbness in the fingertips and weakness in the arms;
- vegetative manifestations;
- increased blood pressure;
- discomfort with movements in the neck;
- constant pain or burning along the spine;
- frequent myositis of the neck muscles;
- posture changes;
- restrictions on head movements;
- may further develop a forced head position;
- tinnitus;
- weather dependency;
- cracking in the neck when performing movements;
- sleep disturbance.

These are the most frequently expressed symptoms that a patient may have. Unfortunately, the process can begin to unfold as early as adolescence and adolescents will file similar complaints.
Most of these symptoms occur together. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine occurs with episodes of exacerbation and remission. This is due to the effect of provoking factors on the body. We must not forget that if a similar diagnosis is made, rehabilitation therapy and a rehabilitation course should be performed every six months to avoid an acute period.
Taking into account that the main reason for the development of the disease is a decrease in the trophism of the intervertebral disc and the lack of adequate therapy, the process can end with the formation of an intervertebral hernia.
Complaints and clinical picture of the disease - photo
Vascular manifestations in the form of dizziness or headache are aggravated by performing elementary motor tasks (tilting or turning the head). In the set of all complaints, the patient tries to take an additional position to reduce symptoms, which worsens the nutrition of the intervertebral disc.
It is these complaints that most often lead the patient to consult a doctor. If treatment is not carried out, the complaints will intensify and become more persistent, that is, they will not disappear on their own.
Pain in cervical osteochondrosis, as a rule, constant, painful and burning character. The disease can be accompanied by periodic "lumbago", which is caused by sudden movements.
An increase in blood pressure in the context of osteochondrosis causes the patient to be examined by a therapist. If proper treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the increase in blood pressure will become permanent, contributing to the development of secondary hypertension. In these situations, a properly compiled anamnesis is of great importance.
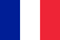
When the process is localized in the cervical spine, the discomfort extends along the back of the neck, the constant tension of the musculoskeletal system contributes to the limitation of movements and the formation of a forced position of the head.
Pain in cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by altered sensation. Due to the constant discomfort, a muscle roll is gradually formed in the shoulder area, palpating the patient experiences discomfort in this area.
In addition to constant discomfort, the patient may experience a sharp, stabbing pain in the neck. The appearance of such complaints suggests that the patient should be given a complete rest to reduce pain. In some cases, the pain is so severe that a person cannot perform the simplest actions (turn the head, breathe deeply, straighten the back). In all cases, the patient should be examined by a doctor and the diagnosis of osteochondrosis should be confirmed.
Changes in hormone levels also play an important role in the development of cervical spine disease. Therefore, a well-chosen physical activity will reduce the general clinical symptoms and alleviate the patient's condition. Due to the fact that neck pain constantly bothers, secondary sleep disturbance occurs. It is difficult for a person to take a comfortable position in bed, he worries, which leads to psycho-emotional stress.
In addition, the patient pays attention to the violation of sensitivity. They are described as "goose bumps" that are felt on the fingertips. In some cases, the discomfort can be localized throughout the arm and muscle strength decreases.
Disease diagnosis
It is quite difficult to make a diagnosis based on an exam. Basically, to clarify the diagnosis, the following activities are carried out:
- full compilation of complaints;
- consultations with specialized specialists (cardiologist, endocrinologist, neurologist);
- X-ray examination of the cervical spine;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
Examinations by specialized physicians are necessary to exclude acute conditions of the cardiological profile and others. With the exclusion of acute somatic pathology, one can speak of the diagnosis of osteochondrosis. In addition to the general clinical manifestations, the diagnosis can be confirmed by an X-ray examination of the spine.
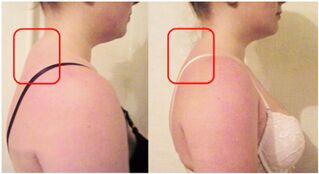
X-rays are the most affordable and easy-to-use test to aid in diagnosis. The image shows a narrowing of the space between the vertebrae, indicating intervertebral disc dystrophy. Bony outgrowths can be distinguished along the edges of the vertebrae. If osteochondrosis is complicated by instability in the cervical spine, then on the radiograph the displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other can be noted.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a disease that can show radiographically which area is most damaged. Even when examining a cervical segment, you can see that the process is not evenly distributed.
In especially difficult cases, an MRI is performed, which helps to diagnose a complication of osteochondrosis - an intervertebral hernia. Thanks to layer-by-layer magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to determine even the smallest hernial changes and immediately indicate the level of the lesion.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine

How to treat cervical osteochondrosis in the acute and interictal period that only a doctor knows. The therapy that is prescribed for this condition must be comprehensive. With an exacerbation of the disease, it includes:
- medications;
- complex rehabilitation therapy (physical therapy exercises, gymnastics, massages, acupuncture, manual therapy);
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, UHF, magnetotherapy, laser therapy);
To prevent exacerbation of osteochondrosis, resort to:
- spa treatment;
- traditional medicine;
- using special bandages and corsets;
- changes in lifestyle (weight loss, balanced physical activity).
Medications for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are as follows:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- drugs that improve blood circulation;
- vitamin complexes;
- in acute situations, analgesics;
- means that it reduces muscle tension.
In addition to pills and injections, creams, ointments and gels are actively prescribed, which are applied to the affected area. By their effect, they contribute to the irritation of the skin in a certain area, which improves blood circulation in the small vessels, thus ensuring the supply of nutrients to the damaged segments and reducing muscle tension.

After an acute period, physical therapy exercises, massages, and physical therapy are scheduled. Rehabilitation therapy is an adjunct to conventional medical treatment. As the condition improves, the nutrition and trophism of the intervertebral disc will also pass better.
During treatment, the patient will notice an improvement in well-being, an increase in efficiency and mood. If treatment is stopped, without completing it, exacerbations of osteochondrosis will pass quite often.
A rehabilitator will tell you how to treat cervical osteochondrosis in the recovery period. Before talking about the complex of rehabilitation therapy, it should be noted that any treatment must be accompanied by correction of bedding. These include orthopedic mattresses and pillows.
Experts also recommend wearing a Shants necklace permanently or for a certain period of time. This method is especially used in children's practice, when patients use it during homework period. The Shants collar is individually selected in orthopedic salons.
An orthopedic pillow for cervical osteochondrosis is selected for each patient. It must be suitable for the size of the bed and selected according to the constitution of the patient. It should not be too small or too large, the main guideline is the width of the person's shoulders.
A pillow for long-term sleep and rest should be of medium firmness and square or rectangular in shape. Other ways are suitable for short breaks. Depending on the activity of the degenerative process, the orthopedic pillow for cervical osteochondrosis must change.
Exercise and gymnastics (lfk)

Rehabilitation therapy should include gymnastics. The main task of the exercises is to strengthen the muscles of the neck and back, the upper shoulder girdle, improve the mobility of the spine and eliminate the muscle clamps. Also, exercises for cervical osteochondrosis affect deeply localized muscles.
As a result of gymnastics in cervical osteochondrosis, physiological curves are gradually restored, and the load on the intervertebral discs decreases. We must not forget that exercises for cervical osteochondrosis should also cover the thoracic segments.
Gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis is performed with an instructor. Helps patients understand which areas need to be emphasized the most. The load and the volume of tasks are selected individually, and depends:
- of the patient's age;
- on the prevalence of the process;
- for the presence of additional comorbidities;
- on the efficacy of pharmacotherapy.
At first they perform simple and not difficult tasks, as the body begins to adapt to new conditions and the muscles do their work with sufficient volume, the exercises become more difficult and the duration of the sessions increases.
Exercise therapy for cervical osteochondrosis includes simple actions. These are tilting the head back and forth, gradually adding circular movements of the head. It must be taken into account that even for physiotherapy exercises there may be contraindications. As a general rule, the complex of a lesson includes tasks aimed at developing and influencing all segments of the column.
After the cervical spine exercises, tasks are gradually added to improve the work of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Physiotherapy exercises for cervical osteochondrosis can be performed standing or sitting. Tasks are performed gradually, at a slow pace, this will allow for additional breathing exercises.
Contraindications for physiotherapy exercises:
- acute pain syndrome;
- increased blood pressure and presence of cardiac pathology in the acute phase;
- coordination disorders and vestibular diseases;
- temperature rise;
- exacerbation of another chronic pathology;
- status after surgical treatment.
Special techniques exercises
This technique is based on the gradual restoration of normal activity of the musculoskeletal system. Gymnastic exercises, which are performed on a specialized simulator, allow you to gradually restore the work of the structures of the cervical spine.
First, pain is relieved, then blood circulation is restored, muscle tension is removed, and classes are held to expand motor activity in the cervical spine. The method is also supported by massage courses, classes in the pool.
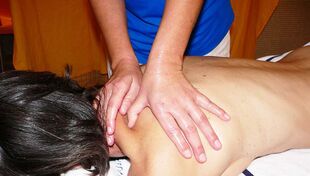
Massage for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
In addition to general strengthening exercises, massage produces a very good effect. Massage for cervical osteochondrosis can be used in different ways (classic, segmental, punctual). In some cases, a combination of different techniques is allowed in one session.
We must not forget that massage for cervical osteochondrosis is performed on a hard surface, face down, and its duration can vary from ten sessions or more. The frequency of repetition of the course is also determined by the attending physician. The effectiveness of the massage will last longer if the patient sleeps on the correct pillow.
Physiotherapy treatments such as magnet or electrophoresis have a local irritating effect. Magnetotherapy is a painless procedure that is well tolerated by both adults and children. The manipulation lasts several minutes, the patient must remain still, so it is recommended more often for older patients.
Electrophoresis is a manipulation that is carried out using a special device. During the procedure, the patient feels a slight tingling sensation generated by the currents. The frequency and impulsivity of the signal are different for each age. This technique is used to inject a medicinal substance that has a positive effect. This manipulation is more aggressive compared to magnetotherapy, so there must be strict indications for its implementation.
This technique is used to inject a medicinal substance that has a positive effect. This manipulation is more aggressive compared to magnetotherapy, so there must be strict indications for its implementation.
A balanced diet is essential in this disease. Patients are advised to eat fruits, vegetables, meat, herbs, fish. You should limit the consumption of salt and all kinds of spices, condiments, smoked or fried, sugar. It is better to drink decoctions and herbal teas, it is advisable to avoid drinking coffee and alcohol.
Traditional medicine is used to reduce pain. Most often, compresses and mixtures are used, which are applied to the affected area. Success in treating osteochondrosis of the cervical spine largely depends on the awareness of the patient. He should not abandon classes and therapy that he started as soon as he feels better. It is irrational to constantly use pain relievers that provide temporary relief, and the disease itself is not treated.